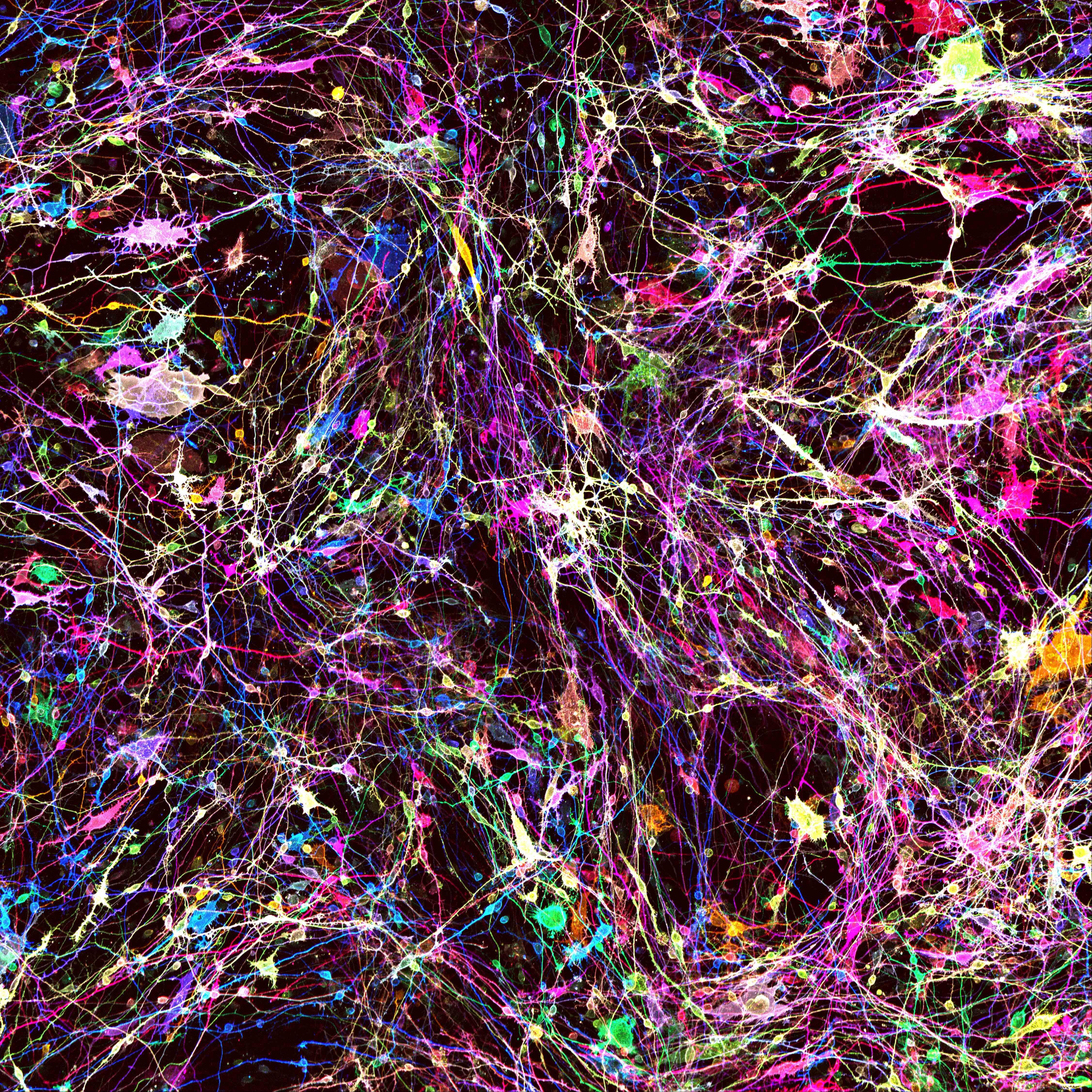
Human genetic studies are finding an ever-growing number of variants associated with psychiatric disease such as Autism Spectrum Disorder and Schizophrenia. Our lab seeks to understand the neurobiological consequences of these variants with high-content measurements of human Pluripotent Stem Cell Derived Neurons (hPSC-Ns). Our approach is to:
- Generate pools of hPSC-Ns of hundreds of genetic backgrounds, either using natural patient variability or experimentally induced targeted changes with CRISPR-Cas9.
- Measure rich (>100's of parameters) fingerprints of thousands of these cells' transcriptomes, electrophysiological properties, and morphological structure with newly developed optical tools.
- Computationally integrate the resulting data sets to generate gene set annotations associated with basic neuronal function and their change in disease genetic backgrounds.
The results of this work will serve to identify common cellular mechanisms in disease states for therapeutic intervention; implement scalable assays for further therapeutic development; and close the circle to further power genetic studies for additional discovery. The work occurs alongside, and benefits from, ongoing tool design efforts occurring in the platform, and is a close collaboration with Dr. Ralda Nehme's lab and with other members of the Stanley Center for Psychiatric Research.